WAEC GCE Leather Work Questions and Answers 2017 | Past OBJ & Essay Expo Answers
Leather Works Questions and Answers: Presently, this is the available West African Examinations Council Leather Goods Manufacturing & Repairs Part 2, for WAEC May/June and and WAEC GCE September/October usually required by GCE students for studying. This past questions and answers are not for expo answer purposes but for students who are willing to use it as a study guide only.
Leatherwork 1 (Objective) and Leatherwork 2 (Essay)
The Leatherwork 1 (objective) and leatherwork 2 (Essay) will be written on tuesday, 29th August, 2017.Both of them will be written on the same day as follows;
- Leatherwork 1 (objective) - 08.30am - 10.30am
- Leatherwork 2 (Essay) - 10.30am - 11.20am
QUESTION 1
- Define Leathercraft.
- Explain any four of the following:
- fat liquoring;
- staking;
- unhairing;
- snuffing;
- bating
In the first place, this question was quite popular among candidates most of whom performed below average. As a matter of fact, the question required the candidates to define Leathercraft and explain some concepts in preparation of leather. Furthermore, most of the candidates mistook leathercraft for leather and gave a poor explanation of some concepts in leather preparation. This prevented them from obtaining the maximum mark.
The candidates were expected to provide the following answers to score higher marks.
(a) It is the practice of making leather into craft objects or works of art, using shaping or colouring techniques. OR It is the art of combining leather with other materials such as fabric, wood, beads, gourd, e.t.c to produce decorative or useful articles using various techniques such as carving, braiding, weaving, sewing, e.t.c.
(b) Look at the following
- It is a method of applying chemically treated oil and fat to leather fibre in order to achieve softness.
- It is a process of softening conditioned pelt either manually or mechanically by pulling and rolling in order make it pliable.
- It is the removal of hairs and other epidermal structures from a soaked hide orskin using sodium sulphide and lime or enzymes.
- It is the abrading of the grain surface of leather in order to remove blemishes.
- It is the treatment of declaimed pelt with enzyme preparations in order to make the grain of the leather smoother and clearer
QUESTION 2
First and foremost, highlight sequentially, the stages involved in the production of a pair of sandals. This question was popular with the candidates. As a matter of fact, the question required candidates to explain the stages involved in the production of a pair of sandals. Generally speaking, most candidates were able to explain just two to three stages without going all the way. On the other hand, this made them to score average marks.
The candidates were expected to provide the following answers to obtain the maximum marks.
- Design the sandal on paper.
- cover the last with masking tape.
- transfer the design on the taped sandal last.
- cut out the design to make a pattern.
- transfer the pattern to make a standard form on cardboard paper.
- mark the patterns and cut them from the cardboard as net pattern.
- using the net pattern, cut out the components of the design from leather leaving lasting and stitching allowance.
- prepare the upper for stitching/closing.
- attach sole unto the upper.
- finishing operations.
- prepare the upper for stitching/closing, by making stitch holes.
- remove the upper from the last and attach the fittings and findings.
- apply glue or adhesive to the upper.
- sew the upper to the sole.
- remove excess adhesive.
- polish the article.
QUESTION 3
Write notes on any three of the following decorative techniques:
- stamping;
- embroidery;
- appliqué;
- dyeing.
A good number of candidates attempted this question and scored relatively high marks. Most of the candidates provided answers to the question but were not able to write extensively on some of the decorative techniques. Candidates were expected to answer thus:
(A). Stamping:
- This is the use of stamps to print patterns on leather surface.
- It is a technique of decorating leather involving the use of shaped implements like stamps.
- Stamps help to create imprints on leather surfaces.
- Stamps are made with the use of mallet to effect prints on leather.
- Commercial stamps are available in various design e.g. geometric shapes, forms of animals, flowers, e.t.c.
- Stamping is mostly performed on vegetable tanned leather that is already dampened with water.
- Water makes leather softer; hence compression of stamp to produce designs becomes simple.
- A design stamped on wet leather becomes permanent as it dries.
- To make impression created with a stamp to last, leather is conditioned with oil and fat.
- Stamping can be effected before or after dyeing.
(B). Embroidery:
- This is the technique of sewing patterns onto leather.
- It is created with stitches.
- It involves the use of needle and thread for light leathers, while awls and thread are preferred for heavy leathers.
- It is a perfect way of effecting permanent decoration on leather.
- It is a way of making bold outlines that are well stitched on leather.
- Patterns can be in geometrical shapes or forms of animals, plant etc.
(C). Appliqué:
- It is an ornamental work made with materials stuck on the surface of leather with the use of glue or stitches.
- It involves fixing a piece or pieces of materials on top of another on the surface of leather to achieve a desired decorative effect.
- Soft and thin leather is best suitable for this type of decoration.
- Tools used include punches, scissors, needles etc .
- Machine is used to sew patterns of larger size on hides, pre-punched stitch holes is required for easy stitching.
- This is done pasting, stitching, sewing different materials onto a leather background to create a design.
(D). Dyeing:
- It is the process of imparting colour onto the leather surface.-
- It involves the use of alcohol based dyes.
- Alcohol helps dyes to get absorbed into the moistened leather quickly.
- Stains can as well be applied to add patterns leaving parts unstained to provide beautiful contrast.
- Alcohol based dyes are more effective than water based dyes.
- Wax paste often serves as final coat.
QUESTION 4
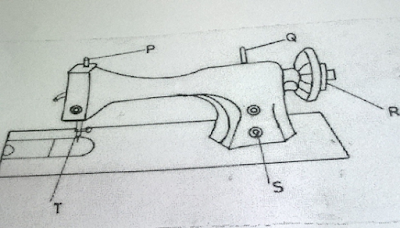
(a). Identify the parts labelled in the diagram below: P; Q; R; S; T.
(b). State one function of each of the labeled parts.
This question was very popular among candidates most of whom scored average marks. Some candidates were able to identify the parts in (a)(i) – (v) but most could not state their functions. Candidates were expected to answer thus:
(a) Answers is here
- P – Pressure regulator.
- Q – Spool pins.
- R – Hand wheel.
- S – Stitch selector.
- T – Presser foot.
(b) Answers is here also
- Pressure regulator – It adjusts the amount of pressure that the presser foot uses to hold the leather down during stitching.
- Spool pins – It is the part that holds the spool thread on the machine.
- Hand wheel – It is the part of the machine that is responsible for themanual movement of the needle. It is also used to wind the thread round the bobbin.
- Stitch selector – It controls the length of stitch
- Presser foot – It helps to keep the fabric flat.
- It also helps to keep the leather firm when sewing.
QUESTION 5
(a) What is the difference between tools and equipment?
(b) State the functions of any four of the following leather crafting tools:
(i) Stanley knife;
(ii) Mallet;
(iii) Thonging chisel;
(iv) Stitch marker;
(v) Rotary punch.
This question was not too popular among the candidates. The few candidates that attempted it were unable to score maximum marks because they could not state in clear terms the functions of the leather crafting tools in the (b) part of the question. Candidates were expected to provide the following answers to score maximum marks in this question.
Tools are working implements utilized with the aid of the hand while equipment are stationed and could be operated mechanically, electrically or manually with both hands and legs. Tools are usually small in size, handful and movable while equipment are usually big, heavy and stationed.
(i) Stanley knife - It is used for cutting thick or heavy leather.
- It is used for cutting straight and curved lines on leather as it comprises both straight and curve blades.
- It is capable of producing shallow, deep and neat cuts on leather.
- It is used for cutting sandal soles.
(ii) Mallet
- It is used to flatten raised surface on leather.
- It is used to flatten the bulk of seam;
- It is used to set a glued join.
(iii) Thronging chisel :
- It is used to produce slit holes.
- The diagonal pronging chisel produces slits that run at an angle to the outer edge of the leather being laced;
- The chisels with few prongs are best for negotiating curves.
(iv) Stitch marker : It serves as a basic tool for measuring and marking holes;
- It is used to make accurate guide marks for punching stitch holes;
- The space of the teeth helps to give even stitch marks on leather.
(v) Rotary punch :
- It is useful for making holes on straps, belts e.t.c ;
- It helps to provide holes for rivets, eyelets e.t.c ;
- It helps to provide variety of holes as the rotating head has six different size punches that can be used at different instances.
QUESTION 6
Explain five factors to be considered when establishing a small scale leather goods enterprise. A good number of students attempted this question and scored relatively high marks. Majority of the candidates who attempted this question were able to list the factors but were unable to expatiate their point to obtain maximum marks .
These candidates were expected to state thus to score maximum marks in this question.
- Availability of capital: Start-up capital and working capital should be made available.
- Room or Space: For the workshop should be available.
- Nearness to source of raw material: The factory must be sited in an area where hides and skins and other raw materials can be easily sourced.
- Nearness to market: The firm should be sited in an area where there is a ready market for leather products.
- Availability of labour: The factory should be sited in an area where there is a large pool of skilled labour in leather craft and manufacturing.
- Adequate transport network: There should be adequate transport network to move raw materials and finished products to the factory and markets respectively.
- Nearness to source of power: The factory should be sited in an area where there is a steady source of power.
- Selecting a business name: The name for the enterprise should be selected appropriately.
General comments on the paper as a whole
The standard of the paper was good. The rubrics were clearly stated and the questions were devoid of any ambiguity. The Marking Scheme was comprehensive and marks were well distributed. Candidates’ performance was a bit below general average.
CANDIDATES’ WEAKNESSES
- Poor expression: Quite a good number of candidates showed great deficiency in expressing their points in clear and simple language. This weakness resulted in poor performance in questions where candidates needed to drive home their points.
- The use of wrong terminologies: Some of the candidates failed to use the correct leatherworks terminologies in providing answers to the questions they attempted. This made it difficult for them to put forward their points which obviously resulted in poor scores.
- Failure to expatiate points: A reasonable number of candidates only identified points but did not go further to explain these points to earn maximum mark
SUGGESTED REMEDIES TO OVERCOME CANDIDATES’ WEAKNESSES
- Candidates need to develop their vocabulary so as to express themselves clearly when writing. Teachers should emphasize this during the course of their teaching.
- Candidate should acquaint themselves with basic leatherworks terms. These terms are necessary in their expression when answering questions in Leather Goods Manufacturing and Repairs.
- Candidates should be encouraged by their teachers to always expatiate their points as this is the only way they could earn good scores in examinations.
CANDIDATES’ STRENGTH
Candidates showed great understanding of concepts; instructions and guidelines were properly followed.
LATEST POSTS
- Requirements for Company Registration in Nigeria | CORPORATE AFFAIRS COMMISSION
- Registering Your Business Names in Nigeria with Cooperate Affair Commission (C.A.C.)
- Advertisement Agencies in Nigeria 2017/2018 | Most Rated Top 10 Online
- Requirements for Contracts in Nigeria - Vendors/Companies/Contractors/Persons
- Starting a Private School in Nigeria | Creche, Nursery, Primary & Secondary School
- Business & Personal Loans in Nigeria with or without Collateral - Apply Now Online