WAEC Health Science Questions And Answers 2018/2019
Read Below For WAEC Questions and Answers For Health Science
Question 1
1.(a) (i) What are enzymes? [ 2 marks]
(ii) State five characteristics of enzymes[ 5 marks]
(iii) Name two enzymes involved in carbohydrate digestion in the body [ 2 marks]
(b) Name the end-product of digestion of
(i) carbohydrates;
(ii) proteins;
(iii) fats. [3 marks]
(c)State two uses each of the following classes of food:
(i) proteins;
(ii) vitamins.[ 4 marks]
(d)State two ways each in which the following substances are important
in the diet of humans:
(i)Roughage;
(ii)Water. [ 4 marks].
Observation: This question was attempted by many candidates and their performance was good. In part (a)(i) candidates were able to define enzyme correctly, however, in part (a)(ii) candidates stated characteristics of enzymes, in part (a)(iii) candidates named enzymes involved in carbohydrate digestion in the body. In part (c) candidates stated uses of proteins and vitamins. In part (d) candidates stated ways in which roughage and water are important in the diet of humans.
The-expected answers were as follows:
l(a)(i) Enzymes
Enzymes are biological/organic catalysts protein in nature, produced in minute quantities in living cells.
(ii) Characteristics of enzymes
- They are made up of protein/protein in nature
- Over heating/excessive heating destroys enzymes
- They work best within a certain specific range of temperature
- They work best within a certain range of PH
- They are specific in action/particular reaction/act on specific substrate
- They remain unchanged at the end of the reaction
- They are activated by co-enzymes/co-factors
- They increase the rate of chemical reactions
- They are required in small amounts.
(iii) Enzymes involved in carbohydrate digestion
- Salivary amylase/ptyalin
- Maltase
- Sucrose
- Pancreatic amylase
- Lactase
(b) End product of digestion of classes of food
(i) Carbohydrates
glucose/simple sugar/fructose/galactose
(ii)Proteins
amino acids e.g. peptones and peptides
(iii)Fats
fatty acid/glycerol.
(c) Uses of the following classes of food
(i)Proteins
- Formation of enzymes, hormones, antibodies and hairs
- Growth/formation of new cells.
- Repair of body tissues
- Release of energy.
(ii)Vitamins
- Required in the absorption of calcium or phosphorus
- Important in the formation of bones
- Prevents rickets/Aids healthy growth
- Prevents deficiency diseases/named diseases.
(d) Importance of the following substances in the diet human
(i) Roughage
- Aids digestion and adds to the food bulk
- It helps the food to pass through the digestive system easily/easy movement of the
- Bowel/prevent constipation
- It reduces the risk of bowel cancer
(ii) Water
- Serves as a solvent for digestion
- Softens the food
- Medium for enzyme/chemical activity
- Transport of digested food
- Forms 70% of body fluid
Question 2
(a)Explain the following terms:
(i) shock;
(ii) fainting. [4 marks]
(b) (i) State three symptoms of shock [3 marks]
(ii) Outline the steps taken in the first aid treatment of shock victims.[ 5 marks]
(c)Explain the following terms:
(i) kyphosis;
(ii) scoliosis. [4 marks]
(d)Explain the following terms associated with bone injuries:
(i) dislocation;
(ii) sprain [4 marks]
Observation: This question was attempted by many candidates and the performance was fair. In part (a) (i) and (ii) candidates could not explain the terms shock and fainting correctly however, some candidates lost marks due to misplacement of definition of shock for fainting and fainting for shock. In part (b) (i) candidates could not state symptoms of shock correctly, in (b) (ii) candidates lost marks due to their inability to outline the steps taken in the first aid treatment of shock victims. In part (c) candidates explain khyphosis and scoliosis correctly because of their constant familiarity with the terms. In part (d) candidates also explained dislocation and sprain due to their familiarity.
The expected answers were as follows:
(a) Explanation of the following terms
(i) Shock
It is a dangerous condition arising from severe injury or emotional strain that prevents
enough oxygenated blood to reach vital organs of the body e.g. brain, heart.
(ii) Fainting
Is temporary loss of consciousness due to reduced supply of oxygenated blood to the
brain.
(b) (i) Symptoms of shock
- Sluggishness
- Cold clammy skin/sweating
- Pale face
- Shallow breathing
- Weak rapid pulse
- Vomiting
- Thirst
- Fainting/loss of consciousness
(ii) Steps taken in first aid treatment of shock victim
- Correct the cause of the shock e.g control bleeding, disconnect electricity source etc.
- Keep victim lying down on his back
- Keep air passage open
- If vomiting turn head to one side
- Keeping head lower than body by elevating legs if no bone is broken
- Reassure the victim/calm victim down
- Avoid over crowding
- Take to hospital/consult a doctor
(c) Explanation of the following terms
(i)Kyphosis
This is an exaggeration of the backward curve, of the thoracic vertebrae, in extreme
cases it is known as hunchback.
(ii) Scoliosis
This is the lateral curvature of the spine in the upper or lower part of the spine.
(d) Explanation of the following terms
(i) Dislocation
It is an injury which occurs when bones at ajoint move away from its original
position/displacement of one or more bones at the joint.
(ii) Sprain
An injury/wrenching or tearing of ligaments or other structures in a joint.
Question 3
(a)(i) What is an endocrine gland? [2 marks]
(ii) State three functions of adrenalin. [3 marks]
(b) State three effects of each of the following conditions in humans:
(i) over-secretion of thyroxin;
(ii) under-secretion of thyroxin.[6 marks]
(c) (i) Write HIV in full. [ 1 mark]
(ii) Distinguish between HIV and AIDS. [2 mark]
(d)State two methods each by which the vectors of the following diseases can be controlled:
(i) onchocerciasis;
(ii) schistosomiasis;
(iii) guinea worm. [ 6 marks]
Observation: This question was attempted by few candidates and candidates performance was fair. In part (a)(i) candidates could not define endocrine gland correctly in (a) (ii) candidates lost marks because they cannot state functions of adrenalin. In part (b) however, candidates lost marks because they mixed up effect of over-secretion of thyroxin with effect of under-secretion of thyroxin. In part ( c) (i) candidates lost marks due to their inability to write HIV in full, some candidates wrote Human immino deficiency while some wrote immune only, in (c) (ii) candidates could not distinguish between HIV and AIDS. In part (d) candidates could not state the method of controlling the vectors of onchocerciasis, schistosomiasis and guinea worm, few candidates that stated the methods mixed up onchocerciasis for guinea worm and schistosomiasis for onchocerciasis.
The expected answers were as follows:
(a)(i) Endocrine gland
Is a gland whose secretion does not pass through any duct/ductless before reaching its target
organ/ductless gland which secretes directly into the blood.
(ii) Functions of adrenal in
- Increasing the rate of conversion of glucose to glycogen
- Controls response for fight or flight/prepares the body for action
- Increases the rate of heart beat
- It increases muscle tones
- It increases rate of breathing action
- Increases blood sugar level.
(b) Effects of the following conditions in humans
(i) Over-secretion of thyroxin
- Thyroid gland becomes large/goiter develops
- Increases rate of heart beat
- Large appetite is developed
- There is loss in body weight
- Sleeplessness/nervousness/anxiety
- Rate of metabolism is increased
- Increase in blood pressure
(ii) Under-secretion of thyroxin
- Rate of metabolism decreases
- Rate of heart beat decreases
- Body temperature is lowered
- Children become stunted in growth
- Children have poor mental development
- Adults develop thick skin.
(c) (i) HIV in full
Human Immuno Deficiency Virus
(ii) Distinguishing between HIV and AIDS
HIV is a virus and AIDS is a disease caused by the virus
(d)Method by which the vectors of the following diseases can be controlled
(i) Ochocerciasis
- Clear bush around banks of river/allow free flow of stream.
- Treat breeding places with insecticides
(ii) Schistosomiasis
- Introduce fish to eat intermediate host (water snail)
- Eliminate the water snail with mollusc ide
- Clear vegetation around pond/destroy breeding grounds
- Prevent infected person from urinating or defecating into waters
- Avoid bathing in infected water.
(iii)Guinea worm
- Boil drinking water/provide good source of water.
- Filter water before drinking
- Avoid wading or bathing in water/streams.
- Rivers/lakes/ponds wear rain boot.
- Destroy intermediate host.
Question 4
Study the diagrams below and use them to answer questions 4(a) and 4(b).
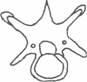
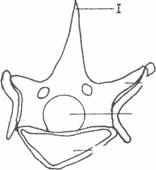
Fig. 1 b
(a) (i) Identify the structures illustrated in Fig 1 a and Fig. 1 b [2 marks]
(ii) Name the parts labeled, I, II, III and IV. [2 marks]
(iii)State one function each of the parts labeled I, II, III and IV. [ 4 marks]
(b) (i) In which region of the human body can the structure in Fig. 1 a be found? [ 1 mark]
(ii) State three differences between the two structures
illustrated in Fig. 1a and Fig.1b [3 marks]
(c) Name the four chambers of the heart [4 marks]
(d) State the function of each of the following:
(i)pulmonary artery;
(ii)pulmonary vein;
(iii)biscuspid valve;
(ivsemi-lunar valve. [ 4 marks]
Observation: This question was attempted by few candidates and candidates performance was poor. In part (a) (i) candidates identified the structures wrongly, in (a)(ii) candidates mixed up parts labelled in their answers, in (a) (iii) candidate stated wrong function of the parts labelled I, II, III and IV.
In part (b) (i) candidates could not mention region of the human body where the diagram can be found, in (b) (ii) candidates could not also state differences between the two structures thoracic vertebra and cervical vertebra. In part (c) candidates mentioned chambers of the heart. In part (d) candidates could not state the function of pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, biscupid valve and semi-lunar valve.
The expected answers were as follows;
(a) (i) Identification of the structures illustrated
fig 1a thoracic vertebra
Fig 1a cervical vertebra
(ii) Naming the parts labelled
- Neural spine
- Transverse process
- Neural canal
- Centrum
(iii)Function of the parts labelled
Function of 1
attachment of muscles to bones
Function of 2
attachment to the rib
Function of 3
for the passage of spinal cord.
Function of 4
it fits into the intervertebral disc/provides rigidity to the bones.
(b)(i) Region of the human body in which the structure in fig l a be found is
Thoracic region
(ii) Differences between fig la and fig. lb
Fig l a Fig 1 b
Centrum is small Centrum is large
Short neural spine Long neural spine Small netrual canal Large neural canal
Short transverse process Long transverse process
Presence of vertebraterial canal Absence of vertebrate rial canal
Absence of facets. Has facets for attachment of ribs
(c) Naming the four chambers of the heart
- Right atrium/auricle
- left atrium/auricle
- right ventricle
- left ventricle
(d)Function of each of the following:
(i)pulmonary artery;
Carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
(ii)pulmonary vein;
Carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
(iii) biscuspid valve;
Prevent back flow of blood from left ventricle to atrium
(iv)semi-lunar valve.
Prevents back flow of blood from aorta left ventricle/pulmonary
artery right ventricle.
Question 5
(a) (i) What is ventilation? [2 marks]
(iiState five factors that may be considered to ensure proper ventilation When building a home [ 5 marks]
(iii) Give four reasons why proper ventilation is necessary for humans [4 marks]
(b) State five ways of preventing tooth decay. [5 marks]
(c)State two causes each of
(i) constitution;
(ii) indigestion. [ 4 marks]
Observation: This question was attempted by many candidates and candidates performed fairly well. In part (a)(i) candidate could not define ventilation, in (a)(ii) candidate could not state factors that may be considered to ensure proper ventilation when building a home correctly, in (a)(iii) candidates gave reasons why proper ventilation is necessary for humans. In part (b) candidates stated ways of preventing tooth decay. In part (c) (i) and (iii) where candidates were requested to state causes of constipation and indigestion candidates stated the causes correctly.
The expected answers were as follows:
(a)(i) Ventilation
It is a process of displacing state air, with fresh in a room/an enclosure/environment
(ii) Factors considered to ensure proper ventilation when building a home
- Size of the windows
- Position of windows
- Alignment of the building
- Direction of wind flow in the area
- Height of the ceiling
- Adequacy of number of windows
- Ventilator bricks/perforated walls/ air ways
(iii)Reasons why proper ventilation is necessary for human
- Prevention of suffocation/sweating
- Removal of state air/recycling of air
- Removal of excess heat
- Removal of body odour/pollutants
- To reduce bacteria/microbes
- Reduces the incidence of respiratory diseases
(b)Ways of preventing tooth decay
- Teeth must be kept clean/brushed after meals
- Avoid eating too many sweets
- Regular visit to the dentist
- Eating food rich in calcium/phosphorus
- Avoid eating too hot or cold food to prevent cracking
- Avoid using the tooth to open bottle tops
- Use fluoride tooth paste/drink fluorinated water
- Avoid using sharp/pointed object to pick the teeth
- Reduce the intake of carbonated drinks.
(c) (i) Causes of constipation
- Lack of exercise
- Absence of roughage in the diet
- Absence of fruits/vegetable in diet
- Intake of too much dry food/junk food/over eating
- Not taking sufficient water
(ii) Causes of indigestion
- Eating at irregular times
- Improper chewing
- Over heating
- Heavy smoking
- Emotional stress
- Stomach ulcer
- Inadequate cooking.
