WAEC GCE Biology Past Questions and Answer 2017/2018 | OBJ/Theory & Practical Answer
WAEC GCE 2017 Biology Practical Answer for Theory – Nov/Dec Expo
Question 3
- (a)(i) What is sewage? [2 marks]
- (ii) State five effects of releasing untreated sewage into a stagnant water body. [5 marks]
- (b) Explain surface terracing as a soil conservation method. [3 marks]
- (c) Explain the term adaptation. [2 marks]
- (d) Explain two ways each by which the following organisms adapt to their habitats:
- (i) hydrophytes; (ii) xerophytes. [8 marks]
Observation
Candidates failed to define sewage satisfactorily; some regarded sewage as refuse. Question 3 (a) (ii) was poorly answered. They could not give the effects of releasing sewage into a stagnant water body.
Question 3 (b) was not well answered and poorly attempted.
Adaptation was not properly defined too. Candidates could explain ways by which hydrophytes adapt to their habitat but could not explain well for xerophytes.
The expected answers are:
(a) (i) Sewage
Waste matter/faeces, urine, waste water from animals/industrial/domestic sources; that is dissolved/suspended in water.
(ii) Effects of releasing untreated sewage into a stagnant water body
- Spread of water-borne diseases/correctly named diseases/microbes/pathogens;
- May be toxic/poisonous to aquatic life/organisms;
- Makes water unfit for consumption/use;
- Increased decomposition;
- Increased concentration of nutrients;
- Rapid growth of algae/aquatic plants/algal bloom/eutrophication;
- Depletion of oxygen;
- Suffocation/death of aquatic animals;
- Generates offensive odour/air pollution;
- Nutrient/nitrate/phosphate enrichment/accumulation in a water body; as a result of breakdown by bacteria.
(b) Surface terracing as a soil conservation method
A method of controlling erosion on a gentle/steep slope of hill; flat horizontal areas are constructed on which crops are cultivated; following the contour; steps/walls are built along the contours; ploughing is also done along the contours; reduces the speed of water running down the slopes.
(c) Adaptation
Is the possession of the characteristic/trait/behaviour/structure/feature; that evolved over a period of time; enable an organism to survive and reproduce; in response to changes in the environment/habitat.
(d) Adaptation of
(i) Hydrophytes:
- Some hydrophytes lack/have reduced roots/root hairs/root caps;
- do not need firm anchorage in water/wetland;
- presence of large air space/aerenchyma in roots/leaves; provide support for bouyancy;
- presence of hairs on the leaves; to prevent blockage of the stomata;
- stomatal pores; occur only at the upper epidermis of the leaves to aid transpiration/loss of water;
- numerous adventitious roots and root hairs; aid the absorption of water/mineral salts;
- small size of the plant; for buoyancy/floating in water;
- waxy upper surface of the leaf; to prevent clogging of the leaf by water;
- long petiole/leaf stalk to support/expose the broad lamina for photosynthesis;
- long flower stalk/pedicel; to expose flower for pollination/pollinating agents;
- presence of breathing roots/pneumatophores; for breathing/gaseous exchange.
(i) Xerophytes:
- possession of thick succulent leaves/stem; for storing water;
- reduction of leaves to spines; to reduce water loss/rate of transpiration;
- thick waxy cuticle on epidermis; to reduce water-loss/transpiration;
- possession of long tap root system; to obtain water from great depth of soil;
- presence of sunken stomata; to reduce water loss;
- reduced number of stomata; to prevent excessive water loss;
- possession of multiple epidermal layers; for water conservation/to reduce water loss.
NOTE: Structure x1
Function x1; Function alone will not score.
Function must correspond with structure to score.
Question 4
(a) Explain the following terms:
(i) test cross;
(ii) monohybrid cross. [4 marks]
(b) In a mango plant, the allele for bean-shaped seed is r and is recessive to round-shaped seed R. With the aid of a genetic diagram, determine the genotypes of the offspring if a homozygous bean shaped parent is crossed with a homozygous round shaped parent. [16 marks]
Observation
This was the most unpopular question among the candidates. Many candidates could not explain Test cross satisfactorily. Majority of the candidates that attempted 4b scored good marks with the exception of those that could not cross properly.
The expected answers are:
(a) (i) Test cross: This is the crossing/mating of an organism of unknown genotype; with a homozygous recessive/double recessive organism; to determine the genotype of an organism.
(ii) Monohybrid cross: This is a genetic cross between parents; that differ in the alleles they possess; for one particular gene
(b) Crosses
(i) R-Round seed
r- bean-shaped seed
Parental genotype (homozygous) RR X rr
Gametes R R X r r
Correct crossing (CC)
F1 generation (Genotype) Rr Rr Rr Rr
Question 6
(a) Copy and complete the table below. [6 marks]
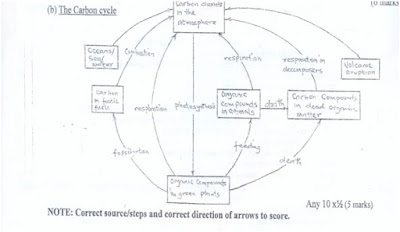
(b) Make a labelled diagram of the carbon cycle. [5 marks]
(c)(i) What is an Estuarine habitat? [2 marks]
(ii) Construct a food chain typical of an Estuarine habitat. [2 marks]
(d)(i) Name two pests and two diseases that can attack plant crops. [4 marks]
(ii) State three ways of controlling plant diseases. [3 marks]
(e) State four functions of a public health authority. [4 marks]
(f) State four ways of maintaining food hygiene in the community. [4 marks]
Observation
Question 6(a) was fairly answered.
- Diseases, One effect and One remedy
- Kidney stones
- Nephritis
- Diuresis
Majority of the candidates drew the Carbon cycle without showing the direction of flow with arrow heads. Some candidates could not link the activities with CO2 production. Majority of the candidates answered questions 6 (c) (i) and (ii) quite well but could not show the direction of the arrows in (c) (ii), the food chain properly.
Questions 6 (d) (i) was well attempted but for bad spelling of the technical terms. Candidates performed poorly when stating the answers to questions (e) and (f).
The expected answers are:
6. (a) Kidney diseases
Diseases
- Kidney stones
- Nephritis
- Diuresis
One effect Each Above
- Abdominal pains; decreased frequency of urination; pains during urination; presence of blood in the urine; increased blood pressure.
- Oedema/swelling of feet and ankle; high blood pressure; blood in urine/blood cells in urine/dizziness/back pain/fatigue;/general weakness; inflammation of the kidney tubules.
- Thirst/dehydration occurs; high blood pressure may occur; loss of appetite; weakness; fatigue; nausea; loss of serum electrolyte.
One remedy from Each Above
- Drink plenty of water
- Kidney transplant; avoid foods rich in calcium/red meat/meat; consult a physician.
- Consult a physician; kidney transplant; dialysis/all food items must be washed/cooked properly; drinking water boiled/filtered/sterilized
- Consult a physician; avoid fans/air conditions in cold weather; avoid excessive drinking of alcohol.
(b) Diagram - Carbon Cycle
(c) (i) Estuarine habitat
Is the place/point where a river enters the ocean/sea; into which the tides flow; fresh water mixes with water; to form brackish water.
(ii) Food chain typical of an estuarine
Phytoplanktons barnacles fish bird OR
Detritus worm mollusc bird OR
Detritus shrimp fish bird
All must be correct to score
Correct sequence (CS) x 1 mark
Correct direction with arrow (CD) x 1 mark
(d) (i) Pests that can attack plant crops
Stem borer; army worms; weevils; black tea-thrips; aphids; root mealybugs; variegated grasshopper; beetle; rodents; squirrel; locust; birds; mites; cotton stainer; any correctly named examples.
NOTE: Spelling must be correct to score.
Diseases that can attack crops
Leaf spots; cankers; rosette; rice blast, root knots; swollen shoot of cocoa; sigatoka; black pod of cocoa; freckle; root/stem rots; bacteria blight; smut; downy mildew; powdery mildew/ any correctly named disease.
NOTE: Spelling must be correct to score.
(ii) Ways of controlling plant diseases
- Chemical control/ use of fungicides/nematicides/bactericides/pesticides;
- Biological control/use of predators and parasites of insects/pests to keep them in check;
- Breeding resistant varieties of crop;
- Planting genetically modified crops that can resist viruses/bacteria transmitted by pests;
- Destruction of infested crops by burning/deep burial/pruning of affected parts;
- Destruction of alternate host
- Adopt good management/crop rotation.
(e) Functions of a public health authority
- ensures cleanliness of public places/markets/schools/playgrounds;
- concerned with the proper disposal of refuse;
- provides maternity clinics/health centres/nursing homes/family planning;
- provides child welfare services;
- provides medical inspection of schools;
- registers birth/death;
- prevents/controls infectious diseases/administers vaccination/immunization/inoculation;
- informs World Health Organization of the outbreak of infectious diseases;
- ensures adequate provision of clean water to the public;
- provides ambulance services;
- provides quarantine services for plants/animals/humans;
- gives health certificate to travellers;
- provides public health education/awareness of diseases;
- inspects and certifies health of animals and cleanliness of slaughter house/abattoir.
(f) Ways of maintaining food hygiene
- proper harvesting/storage methods must be ensured to prevent damage to food items;
- food items must be properly washed/cleaned to prevent contamination;
- food items must be properly cooked at appropriate temperatures;
- kitchen/cooking areas must be kept clean always/free from germs;
- perishable food items must be properly preserved/refrigerated;
- proper personal hygiene must be observed by those handling food;
- cooking utensils must be properly washed/cleaned before and after use;
- cooked/prepared food must be covered at all time;
- proper disposal of unused/leftover food.
Searches related to waec biology 2017
- 2017 waec biology practical answers
- waec 2017 biology practical answer
- waec biology practical question and answer
- waec biology practical 2017
- waec biology specimen 2017
- biology practical questions and answers
- waec specimen 2017
- 2017/2018 waec specimen
General Comments
The standard of the paper compared favorably with those of the previous years. The questions were properly framed and drawn from a wide range of the syllabus. The rubrics were clear. The marking scheme was exhaustive and adequate.
The performance of Candidates this year was poorer than that of last year with a raw mean score of 25 and standard deviation of 11.87 when compared with the raw mean score of 29 and the standard deviation of 12.37 of M/J 2014 WASSCE.
The total number of candidates that sat for the examination was 1,182,038.
CANDIDATES’ WEAKNESSES
The observed weaknesses are as follows:
- wrong spelling of technical terms e.g grass hopper, weevil for grasshopper, weevil;
- describing photosynthesis instead of stating how the leaf is adapted for photosynthesis;
- not attempting the compulsory question 6;
- inability to state correctly the differences between the excretion in flowering plants and excretion in humans;
- lack of sequence in the Carbon cycle;
- inability to define test cross correctly;
- making a diagram of the Nitrogen cycle instead of the Carbon cycle;
- poor crossing of the genetic expression;
- constructing a food chain without showing the direction with arrow heads;
- poor understanding of sexual reproduction in Rhizopus;
- poor attempt in answering questions requiring detailed explanations;
- poor response to questions on ecology and genetics.
The following solutions were proffered to overcome these weaknesses;
- teachers should teach students how to use arrow heads to show the direction of processes in biological cycles;
- students should be taught how to answer questions correctly;
- all the aspects of the syllabus should be touched by the teacher and students;
- students should be more confident when taking examinations;
- students should read and understand a question properly before attempting it, e.g candidates were explaining adoption instead of adaptation as required;
- students should study various textbooks not depending on their teachers’ notes only;
- teachers should teach students how to make good diagrams;
- the correct definition of biological terms should be encouraged.
CANDIDATES’ STRENGTHS
The observed strengths of the candidates include;
- ability to present their answers concisely;
- using tables as required to differentiate between the excretion in flowering plants and excretion in humans;
- ability to describe the mode of feeding in Tapeworm;
- adhering to instructions e.g. not answering question 5 which is not peculiar to their country;
- display of knowledge of some of the tested items;
- ability to state the effect and remedy of kidney stones, nephritis and diuresis;
- ability to write legibly;
- ability to state the benefits of including roughage in the diet of humans.
WAEC GCE Biology Practical Specimen & Syllabus 2017 Released
See WAEC GCE Biology Practical Specimen 2017 – Waec Biology Syllabus Released. The West African Examination Council (WAEC) General ...
WAEC GCE Biology Practical Questions 2017 | Check Answers Here
GCE Biology Practical, WAEC GCE Biology Practical, Biology Practical GCE WAEC Questions 2017 | In this article, I will be showing you past ...
2017 waec gce Biology questions & Answers Now Available here ...
TAGS :2017 waec expo , Best WAEC GCE 2017 Expo site, Exam Runs, Free WAEC GCE Answers, Free WAEC GCE Expo, Free WAEC GCE Runs / Runz, Waec ...
WAEC GCE 2017 Biology Practical Answer – Nov/Dec Expo
WAEC GCE 2017 Biology Practical Answer – Nov/Dec Expo. September/October 2017. CLICK THIS BELOW LINK FOR FULL ANSWER.
Above all what’s your take on this 2017 Waec Gce Biology Alternative To Practical Questions And Answers? We believe this article was interesting right, if yes, don’t hesitate using our share button below to inform – friends and relation via Facebook, twitter or Google+. Please follow and like our Facebook page.