WAEC Physics Practical Specimen 2018
Read below For WAEC Practical Specimen 2018
Question 1
A stone is projected vertically upward with a speed of 30 ms" from the top of a tower of
height 50 m. Neglecting air resistance, determine the maximum height it reached from
the ground
[g = 10 ms2].
Observation: Generally, candidates reacted to the given numerical satisfactorily. However, some
candidates failed to go further to determine the height from the ground as demanded by
the question by adding 50m. The expected answer is:
v2 =u2 - 2gx
At maximum height v = 0
o = 302 - 2 x lOx
o = 900 - 20 x
x = 45m.
Height from ground = 50 + 45
= 95m
Question 2
A force of 40 N is applied at the free end of a wire fixed at one end to produce an
extension of 0.24 nun. if the original length and diameter of the wire are 3 m and 2.0 nun
respectively, calculate the:
(a) stress on the wire;
(b) strain in the wire.
Observation: Many candidates messed up with the calculations of the cross-sectional area of the wire as they could not convert millimeters to metres and in the poor handling of the standard form (decimals) Not much difficulty was encountered with the correct formula and computation for strain.
The expected answers are:
(a) Stress = Force = F
Area A
= 40
3.14 (1.0 X 10-3)2
= 1.27 X 10-7 Nm-2
(b) Strain = Extemion or e
Length l
= 0.24 X 10-3
3
= 8.0 X 10-5
Question 3
When a lead-acid accumulator is fully charged, evolution of gases occurs at the electrodes. Name these gases and the respective electrodes at which they are given off.
Observation: Majority of the candidates attempted this question and performed satisfactorily.
The gases were correctly identified but the respective electrodes from which they were evolved were not correctly stated. The expected answers are:
The gases are :
(i) Hydrogen
(ii) Oxygen
The electrodes at which they are evolved:
(i) Hydrogen Anode/lead peroxide
(ii) Oxygen Cathode/lead plate
Question 4
(a) State two factors which affect the mass of elements deposited during electrolysis.
(b) List two non-electrolytes.
Observation: The questions fell a prey to most candidates who validly presented the required correct responses. However, few candidates gave factors affecting selective discharge of elements during electrolysis. The expected answers are:
(a)Any two correct factors e.g
- Time
- Current/quantity of charge
- Nature/e.c.e of element.
(b)Any two correct non-electrolytes e.g
- Water
- Kerosene
- Petrol
- Benzene
- Ethanol
Question 5
(a) Differentiate between plane polarization and interference as applied to waves.
(b) List two uses of polaroids.
Observation: Many candidates failed to give acceptable distinction between plane polarization and interference as applied to waves. However, listing of two uses of polaroids posed no problem to them.
The expected answers are:
(a) Any 2 correct pair e.g.
(b) Any two correct uses of polaroids 2 x 1/2 mark
e.g They are used in:
production of 3-dimentional films
determination of concentration of sugar solution
polaroid cameras
sun glasses.
Question 6
(a) List two examples each of substances with:
(i) Low viscosity;
(ii) High viscosity.
(b) When is a liquid said to be viscostatic?
Observation: Part (a) was well handled by majority of the candidates. For part (b) very few of the responding candidates succeeded in giving the correct meaning of a visco static liquid.
The expected answers are
(a) (i) Any two correct examples e.g.
- Water
- Kerosene
- Ethanol
- Methylated spirits.
(ii) Any correct two examples e.g.
- Palm oil
- Engine oil
- Glycerine
(b) A liquid is visco static if of its viscosity does not change (appreciably) with change in temperature.
Question 7
State one reason each why cathode rays:
(a)are not electromagnetic waves;
(b)cast sharp shadows of objects in their path;
(c) can rotate a light paddle wheel inside a discharge tube
Observation: Candidates' responses were quite poor due to poor understanding of properties of cathode rays e.g. some candidates stated that cathode rays possess energy as against the fact that they possess momentum. The expected answers are:
Because they
(a) are deflected by electric and/or magnetic field(s)
(b)travel in straight paths (rectilinear propagation)
(c)posses momentum
Question 8
An X-ray tube operates at a potential of2500 V. lfthe power of the tube is 750 W, calculate the
speed of the electron striking the target.
[ e = 1.6 x 10-19 C; mass of electron = 9.1 x 10-31 kg]
Observation: Generally, candidates avoided this question, thus rendering it unpopular. Only few quoted the correct formula but substituted wrongly. Those that substitute correctly evaluated it wrongly. The expected answer is:
eV = 1/2mv2
1.6 x 10-19 x 2500 = Yz x 9.1 X 10-31 x v2
v2 = 8.79 X 1014
V = 2.96 X 107 ms2;
Question 9
(a) Write down the names of two particles used in explaining the wave nature of matter
(b)State the wave characteristics which are exhibited by the particles named in (a) above.
Observation: The two parts (a) and (b) were poorly answered by many candidates. Most responding candidates listed all the characteristics of waves instead of listing the two characteristic required.
The expected answers are:
(a) Any correct 2 e.g.
- Electron
- Hydrogen atom/proton
- Helium atom
- Helium nucleus/alpha particle
- Neutron
(b)Wave characteristics exhibited are:
- Diffraction
- Interference
Question 10
(a)State the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle.
(b)The product of the uncertainties in Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle is equal to or greater than a constant. State the mathematical expression for this constant.
Observation
Many candidates could not give the correct statement neither could they reproduce planks constant.
The expected answers are:
(a) It is impossible to determine (accurately) both the wave properties of matter and its particulate properties at the same time OR In any simultaneous determination of the position x and momentum p of a particle, there.
is an uncertainty in its position L\ x and an uncertainty in its momentum ∆p.
(b) 1) ORh
2π
Question 11
(a) Distinguish between perfectly elastic collision and perfectly inelastic collision.
(b)Sketch a distance - time graph for a particle moving in a straight line with:
(i) uniform speed;
(ii) variable speed
(c)A body starts from rest and travels distances of 120,300 and 180 m in successive equal time intervals of 12 s. During each interval the body is uniformly accelerated.
(i)Calculate the velocity of the body at the end of each successive time interval
(ii)Sketch a velocity-time graph for the motion.
Observation: Part (a). Performance was fair. Some of the respondent candidates failed to mention decrease in kinetic energy for the case of perfectly inelastic collision. Some candidates also failed to note that the question highlighted perfectly elastic collision and not ordinary elastic collision.
Part (b). Performance was high for (i), but low for (ii).
Part (c). This part was poorly tackled by candidates due to the use of wrong equations of motion and poor computational skills.
The expected answers are:
(a)Any 2 correct pairs
(c)(i) 1st stage of motion
x = ut + 1/2at2
120 = 0 x 12 + 1/2 X a x 122
a= 5/3
V1 = 5/3 x 12 = 20 ms-1
2nd stage of motion
x = ut + 1/2at2
300 =, 20 x 12 + ½ x a x 122
60 = 72a
a = 5/6
V = 5/6 x 12 = 10
V2= 10 + 20
= 30ms·1
3rd stage of motion
x = ut + 1/2at2
180 == 30 x 12 + ½ x a x 122
180 = 72 a
a = - 5/2
V = -5/2 x 12= -30
V3 = 30 + -30
= 0 ms·1
(ii)
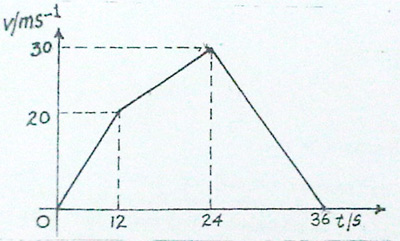
Correct shape of each segment in relation to axes
Origin, (0.0) labeled
Only one axis labeled
Question 12
(a)Explain the terms:
(i) Inertia;
(ii) Inertia mass.
(b)List three factors which affect the rate of evaporation of water in a pond.
(c)Two ice cubes pressed together for some time were found to stick together when the pressure was removed. Explain this observation
(d)Two vertical capillary tubes of the same diameter are lowered into beakers situated at the same level containing liquids A and B of densities 9.2 x 102 kgm -3 and 1.30 x 103 kgm-3respectively. A suction pump is used to withdraw air from the top of the liquid columns in the tubes by means of aT-piece arrangement until the liquid in a rises to a height of26.0 ern. Calculate the height of the liquid in tube B.
Observation: Part (a). Most candidates explained inertia correctly but did not explain inertial mass correctly. Rather they were stating Newton's first law of motion which was not proper.
Part (b). Responses from candidates were satisfactory.
Part (c). Performance was low. Few candidates correctly linked this to regulation but could not explain it as demanded by the question. Some candidates were explaining it in terms of adhesion and cohesion which was wrong.
Part (d). Candidates found this part very tractable.
The expected answers are:
12. (a)(i)Inertia is the reluctance of a body to move if it is at rest or to stop if it is already in motion. The more mass a body has the greater its inertia.
(ii) Inertial mass represents resistance to any type of force whatever the more mass a body has the more force that is required to give it an acceleration. the mass of anobject appearing in the expression
Force = mass x acceleration is the inertial mass
(b)Any 3 correct factors e.g
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Wind
- Area exposed
- Humidity/dryness of the air
( c) Ice melts if ( sufficient) pressure is applied to it. This is because an increase in pressure lowers the melting point of ice. When the two ice cubes are pressed together, melting point of ice is lowered, so they melt to form a thin layer of water (between them). On releasing the pressure, the water formed freezes because decrease in pressure raises the freezing point. Hence the two cubes stick together.
(d)P =pgh
hAPA = hB PB
26xO.92x 103 =hBx 1.30 x 103
hB = 26xO.92x 103
1.30 x 103
= 18.4 cm
Question 13
(a) State two factors which affect the angle of deviation of a ray of light through a triangular glass prism.
(b)Seven virtual images of an object are formed when two plane mirrors are inclined at an angle 0 to each other. Calculate the value of 0
(c)By means of a ripple tank, a student was able to generate series of transverse waves by varying the frequency ofthe dipper and all the waves so generated covered a distance of 0.80 m in 0.2 s.
(i)Determine the speed, v, of the waves
(ii)Copy and complete the table given above in your answer booklet.
(iii)Plot a graph with f on the vertical axis and h -1 on the horizontal axis.
(iv)What does the slope of the graph represent?
f(Hz) λ/m λ -1 /m -1
2.0
4.0
6.0
8.0
10.0
Observation: All the three parts (a), (b) and (c) were commendable responded to by candidates. However, few candidates could not give the correct interpretation of the slope of the graph.
The expected answers is:
The slope represents speed of the wave.
Question 14
(a)
When a positively charged conductor is placed near a candle flame, the flame spreads out as shown in the diagram above.
Explain this observation.
(b)A proton moving with a speed of 5.0 x 105 ms-1; enters a magnetic field of flux density 0.2 T at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic force exerted on the proton.[proton charge = 1.6X 10-19C]
(c)
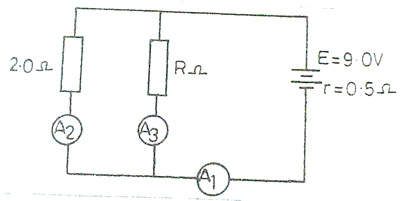
The diagram above illustrates 9.0 V battery of internal resistarIce 0.5Ωconnected to two resistors of values 2.0Ωand R Ω A1,A2 and A3, are ammeters of negligible internal resistances. If A1 reads 4.0 A, calculate the:
(i) equivalent resistance of the combined resistors 2.0Ω and RΩ
(ii) currents through A2 and A3;
(iii) value of R.
Observation: Part (a). Poor responses were given to the expected explanation of the observed spreading out of the candle flame.
Part (b). Correct responses were quite high
Part (c). Generally, candidates did not show enough knowledge of what was required and the attendant mathematical computation due to poor interpretations of the given circuit diagram.
The expected answers are:
14. (a)The candle flame ionizes the air around it. .
The positively charged conductor attracts the negative charges in the air and repels the positive charges.
(b)F = qvB Sin θ .
= 1.6 X 10-19 X 5.0 X 105 X 0.2 X Sin 30°
= 0.8 X 10-1
(c)(i)E = I (Rc + r)
9 = 4(Rc + 0.5)
R: = 9/4-0.5
= 1.75Ω
(ii) Lost volt = Ir = 4.0 X 0.5 =2.0 V
V oltage across 2Ωand RΩ
V = 9.0-2.0 =7.0V
Current in A2 = I2 = V/R2= 7/2 = 3.5A
Current in A3 =I3 = V/R = 7/14 = 0.5A
OR
A3 = A1 - A2
= 4.0 - 3.5 = 0.5A
(iii) 1/RC = 1/R + 1/R2
1/1.75 = 1/R + 1/2
1/R = 1/1.75- 1/2
R = 14Ω
Question 15
(a) State three conclusions that can be drawn from Rutherford's experiment on the scattering of alpha particles by a thin metal foil in relation to the structure of the atom.
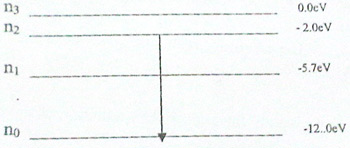
The diagram above illustrates the energy levels of an electron in an atom. If an excited electron moves from n2 to ns. Calculate the:
(i) frequency;
(ii) wavelength
of the emitted radiation.
[h = 6.6 X 10-34 Js; 1eV= 1.6 X 10-19 J; C = 3.0 X 108 ms" ]
(c)The following nuclear equations represent two types of radioactivity.
Identify each type and explain briefly the difference between them.
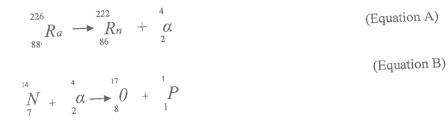
Observation:
Part (a). Performance was fair
Part (b) Candidates registered commendable success.
Part (c) Most of the respondent candidates successfully identified the given equations, A and B.
However, some confused the equation with fusion and fission reactions.
The expected answers are:
(a) Any three correct conclusions E.g.
The nucleus is massive
Most of the atom is empty space
The nucleus is positively charged
Electrons revolve round the nucleus
It explains the periodicity of elements in the periodic table
(b )(i) E20 = E2- E0
= -2.0 - (-12.0)
= 10.0 e V
= 10 x 1.6 x 1O-19J
= 1.6x10-18J
E=hf
Or
f =E/h
= 1.6 x 1018
6.6 x10-34
= 2.424 x 1015 Hz
(ii) c = fλ
λ= c/f
= 3 X 108
2.424 x 1015
(c) A: Natural radioactivity
B: Artificial radioactivity
Any correct difference
